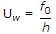ECE :: Electronic Devices and Circuits
-
The maximum rectification efficiency in case of full wave rectifier is
-
For a full wave bridge rectifier supplied with 50 Hz a.c., the lowest ripple frequency will be
-
When an electron rises through a potential of 100 V it will acquired an energy of
-
Which one of the following gain equations is correct for a MOSFET common-source amplifier?
(gm is mutual conductance, and RD is load resistance at the drain) -
If 1 kVA transformer is used for all of the following rectifiers, the d.c. power availability will be least in case of
-
Which of the following is the ferric electric material?
-
The amount of time between the creation and disappearance of a hole in an intrinsic semiconductor material is called
-
In photo electric emission, the threshold frequency f0, work function Uw, and Planck's constant h are related as
-
In which n type device does p substrate extend upto silicon dioxide layer?
-
In a N-type semi-conductor, the concentration of minority carriers is mainly depends on


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook