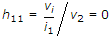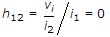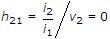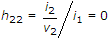ECE :: Electronic Devices and Circuits
-
How is an N-channel junction Field Effect Transistor operated as an amplifier?
-
The Ebers-moll equation for IE in CB configuration is given by
-
Ferrites are
-
The merging of a hole and an electron is called
-
Which of the following semiconductor has the highest melting point?
-
The equivalent circuit of an ideal diode is
-
What is meant by "continuous collector current" in BJT?
-
The small signal input impedance of a transistor whose output is shorted for the measuring signal is
-
Assertion (A): The frequency of light used for photoelectric emission is high.
Reason (R): As per Einstein's equation 0.5 mv2 < hf - Uw.
-
The electric breakdown strength is affected by


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook