Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
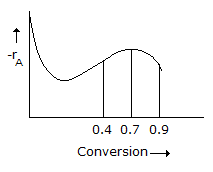
A liquid phase reaction is to be carried out under isothermal conditions. The reaction rate as a function of conversion has been determined experimentally and is shown in the figure given below. What choice of reactor or combination of reactors will require the minimum overall reactor volume, if a conversion of 0.9 is desired ?
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
In a reversible reaction, a catalyst increases the rate of forward reaction
-
Maximum equilibrium conversion for endothermic reaction is obtained at the __________ temperature.
-
When an exothermic reversible reaction is conducted adiabatically, the rate of reaction
-
The rate equation for the reaction represented by,
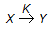 is given by - rx = K1 . Cx/(1 + K2 Cx). At high value of Cx (i.e.., K2Cx > > 1), the order of the reaction and the rate constant are respectively
is given by - rx = K1 . Cx/(1 + K2 Cx). At high value of Cx (i.e.., K2Cx > > 1), the order of the reaction and the rate constant are respectively -
In solid catalysed reactions the diffusional effects are more likely to affect the overall rate of reaction for
-
Helium-mercury method can be used to determine the __________ of the catalyst particle.
-
For the chemical reaction X
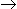 Y, it is observed that, on doubling the concentration of 'X', the reaction rate quadruples. If the reaction rate is proportional to Cxn, then what is the value of 'n' ?
Y, it is observed that, on doubling the concentration of 'X', the reaction rate quadruples. If the reaction rate is proportional to Cxn, then what is the value of 'n' ? -
Chemical reaction rate of a component depends upon the
|
A.
Use of different catalysts in a reversible catalytic chemical reaction does not change the equilibrium composition.
|
|
B.
Alumina is added as a promoter to iron catalyst in ammonia synthesis reaction.
|
|
C.
Activation energy for a reaction is obtained from the intercept of the Ar-rhenious plot.
|
|
D.
Presence of inerts affects the equilibrium conversion of reactants in a chemical reaction.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

