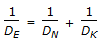Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
In an ideal tubular-flow reactor
-
At a given value of E/R (ratio of activation energy and gas constant), the ratio of the rate constants at 500°K and 400°K is 2, if Arrhenious law is used. What will be this ratio, if transition state theory is used with the same value of E/R?
-
__________ is the controlling step in a highly temperature sensitive fluid-solid non-catalytic reaction.
-
An autothermal reactor is
-
The rate constant of a first order reaction depends on the
-
A reaction in which one of the products of reaction acts as a catalyst is called a/an __________ reaction.
-
Which of the following will favour the reverse reaction in a chemical equilibrium reaction ?
-
Conversion increases with increase in temperature in case of a an __________ reaction.
-
Effective diffusivity (DE) in a catalyst pellet is related to molecular diffusivity (DN) and Knudsen diffusivity (DK) as
-
A photochemical reaction is __________ light.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook