Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Space velocity
-
A reaction which is catalysed by a base is catalysed by all substances which have a tendency to
-
For a homogeneous reaction of nth order, the dimension of the rate constant is given by
-
The fractional volume change between no conversion and complete conversion, for the isothermal gas phase reaction, 2A
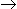 R, is
R, is -
The reaction in which one of the products of reaction acts as a catalyst is called a/an __________ reaction.
-
A typical example of an exothermic reversible reaction conducted at high pressure in industry is
-
Study of chemical kinetics is the easiest in the case of __________ reactions.
-
In autocatalytic reactions,
-
Semibatch reactor is preferred, when a/an
-
Exposure of a photographic plate to produce a latent image is an example of __________ reaction.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

