Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
The conversion in a mixed reactor/accomplishing a reaction A
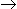 3R is 50% when gaseous reactant 'A' is introduced at the rate of 1 litre/second and the leaving flow rate is 2 litres/second. The holding time for this operation is __________ second.
3R is 50% when gaseous reactant 'A' is introduced at the rate of 1 litre/second and the leaving flow rate is 2 litres/second. The holding time for this operation is __________ second. -
The size of plug flow reactor (PFR) for all positive reaction orders and for any given duty, is __________ that of mixed reactor.
-
A space time of 3 hours for a flow reactor means that
-
The experimentally determined overall order of the reaction, A + B
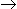 C + D, is two. Then the
C + D, is two. Then the -
In a continuous flow stirred tank reactor, the composition of the exit stream
-
Recycling back of outlet stream to the reactor from an ideal CSTR carrying out a first order liquid phase reaction will result in __________ in conversion.
-
The energy balance equation over a tubular reactor under transient conditions is
-
Which of the following factors control the deactivation of a porous catalyst pellet ?
-
Transition state theory gives the rate constant as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

