Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Arhenious equation shows the variation of __________ with temperature.
-
When a catalyst increases the rate of chemical reaction, the rate constant
-
In which of the following reactions, the equilibrium will shift to the right, if the total pressure is increased?
-
The catalyst in a first order chemical reaction changes the
-
Oil is hydrogenated using nickel catalyst in a __________ reactor.
-
The performance equations for constant density systems are identical for
-
Reaction rate of a first order reaction, which is half completed in 23 minutes will be
-
Which of the following is the optimum operating condition for an exothermic reversible reaction taking place in a plug-flow reactor ?
-
The half life period 't' of a zero order reaction,
 , is equal to
, is equal to -
The point selectivity of the product 'Y' in the reaction,
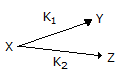
is equal to


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


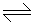 2HCl
2HCl