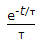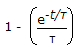Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
For the same residence time, which one will give the maximum conversion ?
-
__________ gas is normally employed in B.E.T.method of finding out the surface area of catalyst.
-
The exit age distribution curve E(t) for an ideal CSTR with the average residence time, τ, is given by
-
The rate constant of a reaction depends on the
-
For the reversible reaction A
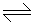 2B, if the equilibrium constant K is 0.05 mole/litre; starting from initially 2 moles of A and zero moles of B, how many moles will be formed at equilibrium ?
2B, if the equilibrium constant K is 0.05 mole/litre; starting from initially 2 moles of A and zero moles of B, how many moles will be formed at equilibrium ? -
For identical flow rate and feed composition, X plug flow reactors (PER) in series with a total volume V gives the same conversion as single
-
Time required for 50% decomposition of a liquid in an isothermal batch reactor following first order kinetics is 2 minutes. The time required for 75% decomposition will be about __________ minutes.
-
For a __________ order reaction, the units of rate constant and rate of reaction are the same.
-
In case of staged packed bed reactors carrying out exothermic reaction, use
-
Vegetable oils are hydrogenated in a __________ reactor.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook