Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
In a semi-batch reactor
-
A trickle bed reactor is the one, which
-
The excess energy of the reactants required to dissociate into products is known as the __________ energy.
-
In a/an __________ vessel, the fluid enters and leaves following plug flow.
-
Shift conversion reaction
-
The importance of diffusion in a catalyst are increased by
-
A back mix reactor is
-
Which one is the rate controlling step in a solid-gas non-catalytic reaction occurring at very high temperature?
-
The rate of the heterogenous catalytic reaction A(g) + B(g)
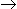 C(g) is given by -rA = k.KA.pA.PB/(1 + KA.PA + Kc.pc), where KA and Kc are the adsorption equilibrium constants. The rate controlling step for this reaction is
C(g) is given by -rA = k.KA.pA.PB/(1 + KA.PA + Kc.pc), where KA and Kc are the adsorption equilibrium constants. The rate controlling step for this reaction is -
For a __________ order chemical reaction,
 , the half life period is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant A.
, the half life period is independent of the initial concentration of the reactant A.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

