Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Which of the following is a controlling factor in very fast heterogeneous reaction ?
-
Enzymes are destroyed, when the
-
For an autocatalytic reactor, the suitable reactor set up is
-
Sometimes, batch process is preferred over continuous process, when the product
-
In a chemical reaction
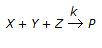 , it is observed that the
, it is observed that the
(i) rate of formation of 'P' is doubled on doubling the concentration of 'X'.
(ii) rate of formation of 'P' is quadrupled on doubling the concentration of 'Y'.
(iii) doubling the concentration of 'Z' does not affect the rate of formation of 'P'.
What is the order of the above chemical reaction? -
The half life period of a first order reaction is given by (where, K = rate constant. )
-
Half life period of a chemical reaction is
-
In the gaseous phase ammonia formation reaction (N2 + 3H2
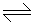 2NH3), the value of the equilibrium constant depends on the
2NH3), the value of the equilibrium constant depends on the -
Transition state theory relates the above quantities as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

