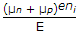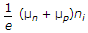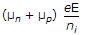ECE :: Electronic Devices and Circuits
-
The atomic number of silicon is 14. It can be therefore concluded that
-
Ohmic range of metal film resistors is
-
The current density J, free electron mobility μn, hole mobility μp , magnitude of free electron and hole concentration ni electric field E and charge on electron e, in intrinsic semiconductor are related as
-
In order to achieve good stabilization in potential divider method current I1 through R1 and R2 should be
-
A sample of N type semiconductor has electron density of 6.25 x 108/cm2 at 300 K. If the intrinsic concentration of carriers in this sample is 2.5 x 1013/cm3 at this temperature, the hole density works out to be
-
Addition of 0.3 to 3.5% silicon to iron
-
A bistable multivibrator
-
Transconductance indicates the


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook