Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Rate of a chemical reaction is not affected by the
-
Overall rate of reaction in a heterogenous catalytic reaction depends upon the mass and energy transfer from the fluid to solid surface and its rate of reaction is usually __________ the concentration of catalyst, if it does not entail a chain mechanism.
-
__________ resistance is not involved in the combustion of a carbon particle.
-
In an ideal P.F.R. at steady state conditions
-
B.E.T. method of finding out surface area of a catalyst, uses the extension of __________ isotherm.
-
In a chemical reaction, repesented by,
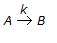 , it is observed that the
, it is observed that the
(i) rate of reaction increases by a factor of 4 on doubling the concentration of the reactant.
(ii) rate of reaction increases by a factor of 9 on trebling the concentration of the reactant.
Then the rate of the reaction is proportional to(where, CA = contentration of the reactant) -
Which of the following holds good for an elementary reaction,
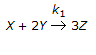 ?
? -
An example of autothermal reactor operation is
-
For a packed bed reactor; the presence of a long tail in the residence time distribution curve is an indication of
-
Space time in flow reactor is
|
A.
The rate of disappearance of 'Y' is equal to the rate of appearance of 'Z'.
|
|
B.
The rate of disappearance of 'Y' is equal to the rate of disappearance of 'X'.
|
|
C.
Three times the rate of disappearance of 'X' is equal to the rate of appearance of 'Z'.
|
|
D.
The rate of disappearance of 'X' is equal to the rate of appearance of 'Z'.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

