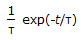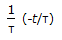Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Catalyst is a substance, which __________ chemical reaction.
-
A rise in temperature
-
The enzyme which can catalyse the conversion of glucose to ethyl alcohol is
-
For reaction, P + 2
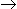 3R, molar rate of consumption of P is
3R, molar rate of consumption of P is -
If pore diffusion is the controlling step in a solid catalysed reaction, the catalyst
-
The conversion of a reactant, undergoing a first order reaction, at a time equal to three times the half life of the reaction is
-
In case of unimolecular type elementary reaction,
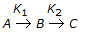 , plug flow reactor as compared to mixed reactor is
, plug flow reactor as compared to mixed reactor is -
What is the value of 'n' if the reaction rate of the chemical reaction A
 B, is proportional to CAn and it is found that the reaction rate triples, when the concentration of 'A' is increased 9 times ?
B, is proportional to CAn and it is found that the reaction rate triples, when the concentration of 'A' is increased 9 times ? -
The first order series reaction
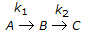 is conducted in a batch reactor. The initial concentrations of A, B and C (CA0, CB0, CC0 respectively) are all non-zero. The variation of CB with reaction time will not show a maximum, if
is conducted in a batch reactor. The initial concentrations of A, B and C (CA0, CB0, CC0 respectively) are all non-zero. The variation of CB with reaction time will not show a maximum, if


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook