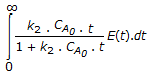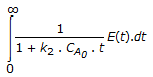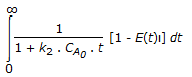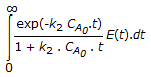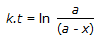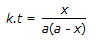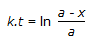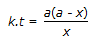Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
A second order reaction of the form A + B
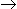 C is called a pseudo-first order reaction, when
C is called a pseudo-first order reaction, when -
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
Effectiveness factor (E) of a catalyst pellet is defined as,
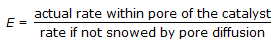 Effectiveness factor for a first order reaction is given by (where, T = Thiele modulus)
Effectiveness factor for a first order reaction is given by (where, T = Thiele modulus) -
Inversion of cane sugar is an example of
-
Pick out the correct statement.
-
In which of the following gaseous phase reactions, the equilibrium of the reaction remains unaffacted by pressure changes ?
-
The mean conversion in the exit stream, for a second order, liquid phase reaction in a non-ideal flow reactor is given by
-
Integral method for analysing the kinetic data is used
-
Concentration of the limiting reactant (with initial concentration of a moles/litre) after time t is (a-x). Then 't' for a first order reaction is given by
-
The rate of a gas phase reaction is given by K . CA . CB. If the volume of the reaction vessel is reduced to l/4th of its initial volume, then the reaction rate compared to the original rate will be __________ times.
|
A.
In a first order reaction, A |
|
B.
Transition state theory approaches the problem of calculating reaction rates by concentrating on the idea of activated complexes. |
|
C.
According to the penetration theory, the mass transfer co-efficient decreases, if the exposure time of an eddy to the solute decreases. |
|
D.
If the rate of an irreversible reaction, A + B |


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


 3O2
3O2