Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
The first order gas phase reaction
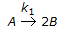 is conducted isothermally in batch mode. The rate of change of conversion with time is given by
is conducted isothermally in batch mode. The rate of change of conversion with time is given by -
The extent of a reaction is
-
Higher free energy of activation of a chemical reaction (at a given temperature) implies
-
Calcination reaction of limestone (CaCO3
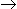 CaO + CO2) goes to completion in the rotary kiln, because
CaO + CO2) goes to completion in the rotary kiln, because -
The reactions with low activation energy are
-
Which of the following is not endothermic in nature ?
-
The rate of an autocatalytic reaction,
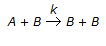 , is given by -rA = k . CA . CB. In this case, the
, is given by -rA = k . CA . CB. In this case, the -
The space time is equivalent to the holding time in a steady state mixed reactor for
-
For the reaction
 , the rate of formation of Z is 0.2 gm mole/litre.hr. what is the rate of disappearance of X in gm mole/litre. hr ?
, the rate of formation of Z is 0.2 gm mole/litre.hr. what is the rate of disappearance of X in gm mole/litre. hr ?


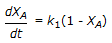


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

