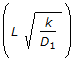Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
An irreversible aqueous phase reaction, A + B
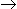 P, is carried out in an adiabatic mixed flow reactor. A feed containing 4kmole/m3 of each A and B enters the reactor at 8m3 /hr. If the temperature of the exit stream is never to exceed 390 K, what is the maximum inlet feed temperature allowed?
P, is carried out in an adiabatic mixed flow reactor. A feed containing 4kmole/m3 of each A and B enters the reactor at 8m3 /hr. If the temperature of the exit stream is never to exceed 390 K, what is the maximum inlet feed temperature allowed?
Data: Heat of reaction = - 50 kJ/mole
Density of the reacting mixture = 1000kg/m3
Specific heat of reacting mixture = 2kJ/kg.K
The above data can be assumed to be independent of temperature and composition. -
For a heterogenous catalytic reaction, A + B
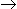 C, with equimole feed of A and B, the initial rate - rA0 is invariant with total pressure. The rate controlling step is
C, with equimole feed of A and B, the initial rate - rA0 is invariant with total pressure. The rate controlling step is -
Half life period of a first order irreversible reaction A
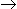 B is
B is -
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
Which of the following is not a dimension-less group used in catalysis ? (where, D = dispersion co-efficient, cm2 /sec.D1 = diffusion co-efficient; cm2/sec L = length of the reactor, cm t = time, sec, v = volumetric flow rate, cm3/sec . V = volume, cm3.)
-
Pick out the wrong statement
-
The energy of activation of a chemical reaction
-
Chemical kinetics can predict the __________ of a chemical reaction.
-
Which of the following fixes the volume of a batch reactor for a particular conversion and production rate ?
-
Volume change for unimolecular type first order reaction
 , increases __________ with time.
, increases __________ with time.
|
A.
Autocatalytic reactions are exemplified by microbial fermentation reactions.
|
|
B.
The slowest step has the greatest influence on the overall reaction rate in case of an irreversible series reaction.
|
|
C.
The fractional conversion at any time is same for both the constant as well as the variable volume system in case of an irreversible unimolecular type first order reaction.
|
|
D.
Hydrolysis of ester in presence of alkali or acid is a zero order reaction.
|
|
A.
For the same conversion, the holding time required in a batch reactor, is always equal to the space time required in a PFR.
|
|
B.
Two mixed reactors of unequal size are available for producing a specified product, formed by a homogenous second order reaction. To achieve maximum production rate, the smaller reactor should be placed in series before the larger reactor.
|
|
C.
Arrehenius equation describing the effect of temperature on rate constant is given by, K = A.e-Ea/RT
|
|
D.
The mechanism for the decomposition of CH3CHO into CH4 and CO in presence of I2 is:
CH3CHO +I2 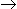 CH3I + HI + CO; slow CH3I + HI + CO; slowCH3I + HI 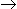 CH4 + I2; fast CH4 + I2; fastThen the rate of disappearance of CH3CHO is equal to K.CCH3I.CHI and acts as a catalyst. |


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook