Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
For nearly isothermal operation involving large reaction time in a liquid-phase reaction, the most suitable reactor is a __________ reactor.
-
What is the Thiele modulus of the solid catalysed first order reaction,
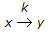 , if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ?
, if the pore diffusion offers negligible resistance to reaction ? -
B.E.T. method can be used to determine the __________ of a porous catalyst.
-
Which of the following is an independent variable for a batch tank reactor with uniform concentration and temperature ?
-
For reactions in parallel viz A
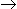 P (desired product) and A
P (desired product) and A 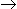 Q (unwanted product), if the order of the desired reaction is higher than that of the undesired reaction, a
Q (unwanted product), if the order of the desired reaction is higher than that of the undesired reaction, a -
For a gaseous phase reaction, rate of reaction is equal to K. CA . CB. If the volume of the reactor is suddenly reduced to l/4th of its initial volume, then the rate of reaction compared to the original rate will be __________ times.
-
In a reversible chemical reaction having two reactants in equilibrium, if the concentration of the reactants are doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
-
The equilibrium constant of a catalytic chemical reaction __________ due to the presence of a catalyst.
-
The rate constant of a chemical reaction increases by increasing the
-
The catalytic activity of enzymes is due to their capacity to lower the __________ energy.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

