Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
When all the limiting reactant is consumed in the reaction, the operational yield __________ the relative yield.
-
The half life period of a first order reaction is
-
The catalyst in a second order reversible reaction increases the rate of the forward reaction
-
Catalyst carriers
-
For the liquid phase zero order irreversible reaction A
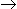 B, the conversion of A in a CSTR is found to be 0.3 at a space velocity of 0.1min-1 . What will be the conversion for a PFR with a space velocity of 0.2 min-1? Assume that all the other operating conditions are the same for CSTR and PFR.
B, the conversion of A in a CSTR is found to be 0.3 at a space velocity of 0.1min-1 . What will be the conversion for a PFR with a space velocity of 0.2 min-1? Assume that all the other operating conditions are the same for CSTR and PFR. -
A high space velocity means that a given
-
In flow reactors, the performance equations interrelate the rate of reaction to the


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

