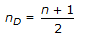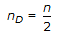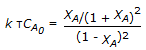Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
During manufacture of H2SO4, the oxidation of SO2 to SO3 by oxygen is an en-dothermic reaction. The yield of SO3 will be maximised, if the
-
The role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction is to change the
-
Molecularity of a reaction
-
BET apparatus is used to determine the
-
When the reaction is dominated by in-traparticle diffusion, the apparent order of reaction (nD) as measured is related to the true order (n) as
-
When the reaction occurs in the diffusion controlled region, the apparent activation energy as measured is only __________ the true value.
-
An isothermal irreversible reaction is being carried out in an ideal tubular flow reactor. The conversion in this case will __________ with decrease in space time.
-
An elementary liquid phase decomposition reaction
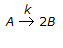 is to be carried out in a CSTR. The design equation is
is to be carried out in a CSTR. The design equation is -
Kinetics of a solid catalysed reaction can best be studied in a __________ reactor.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook