Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
For a solid catalysed chemical reaction, the effectiveness of solid catalyst depends upon the __________ adsorption.
-
Pick out the correct statement.
-
Pick out the correct statement
-
Sulphuric acid is used as a catalyst in the
-
Fractional conversion __________ with increase in pressure for ammonia synthesis reaction i.e., N2 + 3H2
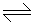 2NH3.
2NH3. -
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
The reason why a catalyst increases the rate of reaction is that, it
-
A first order irreversible reaction, A
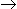 B is carried out separately in a constant volume as well as in a variable volume reactor for a particular period. It signifies that __________ in the two reactors.
B is carried out separately in a constant volume as well as in a variable volume reactor for a particular period. It signifies that __________ in the two reactors.
|
A.
The vessel dispersion number (D/UL) for plug flow and mixed flow approaches zero and infinity respectively.
|
|
B.
Space time in a flow reactor is a measure of its capacity and is equal to the residence time when the density of reaction mixture is constant.
|
|
C.
Mixed reactor is always smaller than the plug flow reactor for all positive reaction orders for a particular duty.
|
|
D.
In an ideal tubular flow reactor, mixing takes place in radial direction and there is no mixing in logitudinal direction.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

