Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Reaction Engineering
-
Which of the following is the most suitable for very high pressure gas phase reaction ?
-
The reaction between oxygen and organic material is a/an __________ reaction.
-
With decrease in temperature, the equilibrium conversion of a reversible endother-mic reaction
-
In an exothermic chemical reaction, the reactants compared to the products have
-
For a reaction of the type,
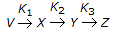 , the rate of reaction (- rx) is given by
, the rate of reaction (- rx) is given by -
In a consecutive reaction system
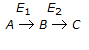 when E1 is much greater than E2, the yield of B increases with the
when E1 is much greater than E2, the yield of B increases with the -
A reversible liquid phase endothermic reaction is to be carried out in a plug flow reactor. For minimum reactor volume, it should be operated such that the temperature along the length
-
The rate constant of a chemical reaction increases by 100 times when the temperature is increased from 400 °K to 500 °K. Assuming transition state theory is valid, the value of E/R is
-
A batch reactor is suitable for
-
For a heterogeneous catalytic reaction
|
A.
free energy of activation is lowered in the presence of catalyst, which remains unchanged at the end of reaction.
|
|
B.
a relatively small amount of catalyst can cause the conversion of large amount of reactants which does not mean that catalyst concentration is important.
|
|
C.
the catalyst does not form an intermediate complex with the reactant.
|
|
D.
the surface of the catalyst does not play an important role during reaction.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

