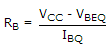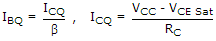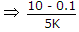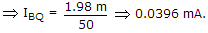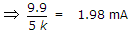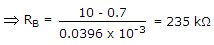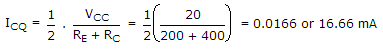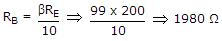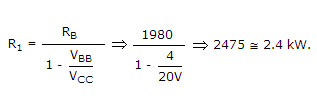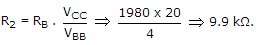ECE :: Analog Electronics
-
In an amplifier the voltage gain is the ratio of
-
Find resistance RB to bring transistor to threshold of saturation VCB = 0, VBE = 0.7 V, a = 0.96
-
The dissipation at the collector is in the quiescent state and increases with excitation in the case of a
-
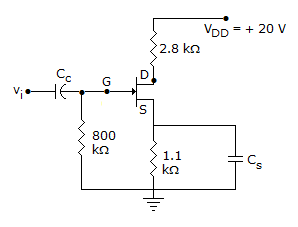
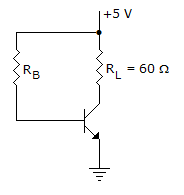
In following circuit, RB will be if VCC = 10 V, VS = 2 V, RC = 5 kΩ, RS = 90 kΩ, β = 50, ICE = 0, VCEsat = 0.1 V
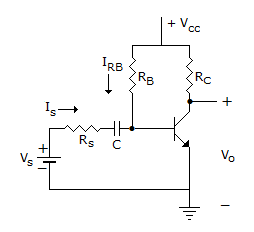
-
In following figure, what will be R1 and R2 for maximum symmetrical swing if VCSat ≈ 0. Given that RE = 200 Ω, RC = 400 Ω, VCC = 20 V, β = 99
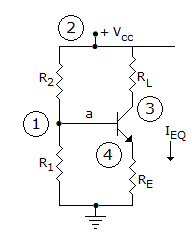
-
The ideal characteristics of a stabilizer is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


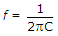
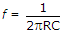
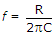
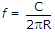
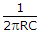 .
.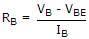
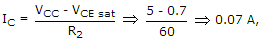
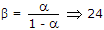
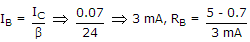
 1.5 kΩ.
1.5 kΩ.