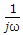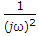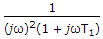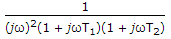ECE :: Automatic Control Systems
-
Optical encoders most commonly used in control systems are
-
The log magnitude curve for a constant gain K is a horizontal straight line at a magnitude 20 log K dB.
-
Transfer functions of even complicated components can be found by frequency response tests.
-
The shape of torque-speed curve of a two phase servo- motor mostly depends on
-
In a lag network the input frequency is 100 fc where fc is critical frequency. The voltage gain is
-
Assertion (A): Temperature control of the passenger compartment of car uses both feed forward and feedback controls.
Reason (R): Feed forward control gives corrective action before the disturbance affects the output and feedback control applies corrective action after output changes.
-
Assertion (A): Most of actual systems are non-linear.
Reason (R): Non linearity may be due to saturation, dead zone, square law etc.
-
The correct sequence of events to improve system stability is
-
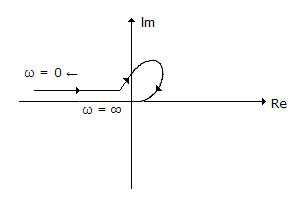
The static equation of a system is
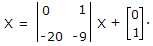 The poles of this system are located at
The poles of this system are located at


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook