ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
The three sides of an admittance triangle denote
-
A step voltage E is applied to an R-L series circuit. At t = 0, the current in the circuit is
-
To find current in a resistance connected in a network, Thevenin's theorem is used VTH = 20 V and RTH = 5 Ω. The current through the resistance
-
In figure, the magnitude of V
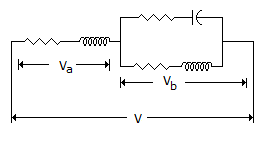
-
A step voltage E is applied to a series R-L circuit. The rate of change of current is maximum at t =
-
The driving point impedance of a network is
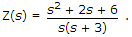 The number of energy storing elements in the network is
The number of energy storing elements in the network is -
Two currents have the same peak value. Wave 1 is sinusoidal and wave 2 is rectangular. The ratio of their heating effects are
-
The following differential equation has
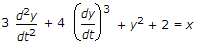
-
If the transmission parameters of the given networks are A = C = 1, B = 2 and D = 3, then the value of Zm is
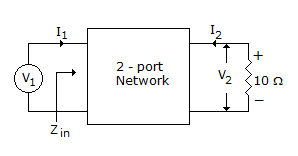
-
The ABCD parameters of ideal n : 1 transformer shown in the figure are
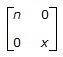 . The value of X will be
. The value of X will be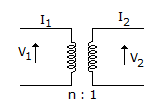


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


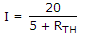
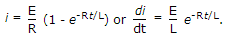
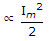 and heating effect of rectangular wave ∝ Im2.
and heating effect of rectangular wave ∝ Im2.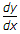 .
.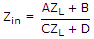 .
.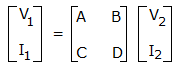
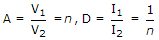 .
.