ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
The poles of an RC function
-
For circuit in figure, which combination of VTH and RTH represents the circuit as seen from ab?
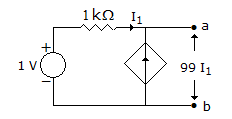
-
Damping ratio =
-
In admittance parameter set, the dependent variables are the currents at the two ports.
-
A constant k low pass filter has fc = 500 Hz. At f = 1000 Hz, the attenuation is
-
If two network is connected in series-parallel connection then
-
For the two ports in figure, y11 = 8 mho, y12 = y21 = -6 mho and y22 = 6 mho. The values of YA, YB, YC respectively are
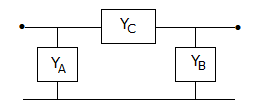
-
Vth = 0, if
-
The electrochemical equivalent of a material


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

