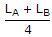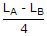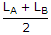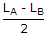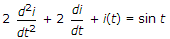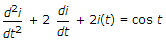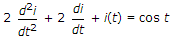ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
If F1(s) and F2(s) are two positive real functions, then the function which is always positive real is
-
The condition AD - BC = 1 for two port network implies that the network is a
-
The units for electrochemical equivalent are
-
Two coupled coils A and B are connected in series. The total inductances in series aiding and series opposing connections are LA and LB. The mutual inductance M is
-
The impedance 3.2 - j 12 in polar form is given as
-
For an R-C impedance function, the residues at all poles are
-
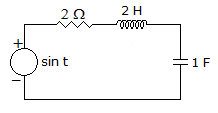
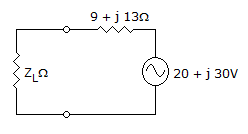
In the circuit shown in figure, maximum power will be transferred when
-
In the analogy between electric and magnetic circuits, flux is analogous to
-
A two port network is reciprocal if and only if

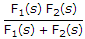

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook