ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
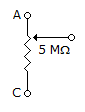
The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals 1 and 2 for the circuit shown in the figure is

-
A dc network has 3 independent nodes and 4 loops. In total analysis, the number of equations is
-
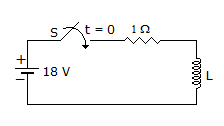
In the circuit, S was initially open. At time t = 0, S is closed. When the current through the inductor is 6 A, the rate of change of current through the resistor is 6 A/s. The value of the inductor would be
-
A series circuit has R = 5 Ω and C = 10 μF. It is switched on to a 12 V dc battery at t = 0. The current in the circuit will be maximum
-
A current of 1 A in the coil of an iron cored electromagnet causes B = 0.5T. If current is 2A, B =
-
Two current sources each of rms value 10 A have frequencies 40 Hz and 50 Hz respectively. They are connected in series, the expression for resultant wave is
-
To find the current in a 20 Ω resistance connected in a circuit, Norton's theorem is used. IN = 7.5 A. The current though 20 Ω resistance.
-
In an R-L-C series circuit, R = 2/L/C . If R is doubled


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


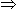 6 = 8 (1 - e-t/L)
6 = 8 (1 - e-t/L) 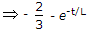
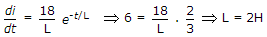 .
.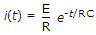 and is maximum at t = 0+.
and is maximum at t = 0+.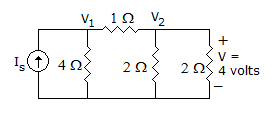

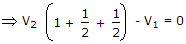
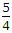 x 8 - 4 = 6A.
x 8 - 4 = 6A.