ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
A square current wave of magnitude 1 A is applied to an element for 5 seconds. The voltage across the element rises linearly from 0 to final value linearly. The element is
-
A periodic voltage v(t) = 1 + 4 sin ωt + 2 cos ωt is applied across a 1 ohm resistance. The power dissipated is
-
A constant k high pass p section has a characteristic impedance of 300 Ω at f = ∞ . At f = fc, the characteristic impedance will be
-
Figure shows a dc circuit. The Thevenin's equivalent circuit at terminals a - b is
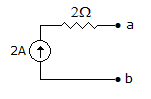
-
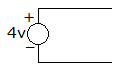
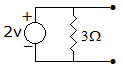
The dependent current source shown in given figure.
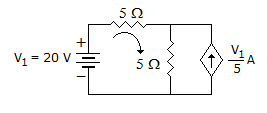
-
The current flowing through the resistance R in the circuit in the figure has the form 2 cos 4t, where R is
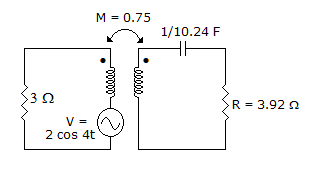


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


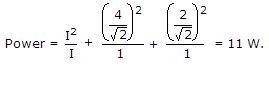
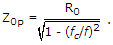 At f = fc, Z0p = infinite.
At f = fc, Z0p = infinite.
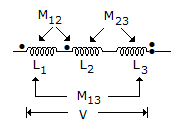
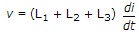
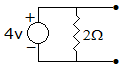
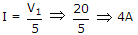
 16 x 5
16 x 5 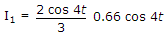
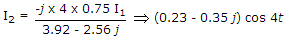 .
.