GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Chemical
- The main unit processes used for the production of hydrogen from natural gas are steam reforming (SR), pressure swing adsorption (PSA), low temperature water gas shift reaction (LT WGS) and high temperature water gas shift reaction (HT WGS). The correct sequence of these in the plant is
- A thermometer initially at 100°C is dipped at t = 0 into an oil bath, maintained at 150°C. If the recorded temperature is 130°C after 1 minute, then the time constant of thermometer (in min) is
- The Bode stability criterion is applicable when
-
The one - dimensional unsteady state heat conduction equation in a hollow cylinder with a constant heat source q is
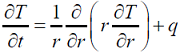 If A and B are arbitrary constants, then the steady state solution to the above equation is
If A and B are arbitrary constants, then the steady state solution to the above equation is - The Newton “ Raphson method is used to find the roots of the equation f(x) = x - cos Ï€x 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. If the initial guess for the root is 0.5, then the value of x after the first iteration is
- An insulated, evacuated container is connected to a supply line of an ideal gas at pressure Ps, temperature Ts and specific volume Vs. The container is filled with the gas until the pressure in the container reaches Ps. There is no heat transfer between the supply line to the container, and kinetic and potential energies are negligible. If CP and CV are the heat capacities at constant pressure and constant volume, respectively (Ï’ = CP/CV), then the final temperature of the gas in the container is
- Consider a binary liquid mixture at constant temperature T and pressure P . If the enthalpy change of mixing, ∆H = 5x1x2, where x1 and x2 are the mole fraction of species 1 and 2 respectively, and the entropy change of mixing ∆S = -R[x1 ln x1 + x2 ln x2] (with R = 8.314 J/mol.K), then the minimum value of the Gibbs free energy change of mixing at 300 K occurs when
- A bed of spherical glass beads (density 3000 kg/m3 diameter 1 mm, bed porosity 0.5) is to be fluidized by a liquid of density 1000 kg/m3 and viscosity 0.1 Pa.s. Assume that the Reynolds number based on particle diameter is very small compared to one. If g = 10 m/s2 then the minimum velocity (in m/s) required to fluidize the bed is
-
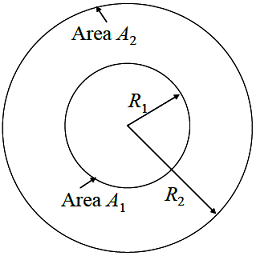
For the enclosure formed between two concentric spheres as shown below (R2 = 2R1), the fraction of radiation leaving the surface area A2 that strikes itself is
- Heat is generated at a steady rate of 100 W due to resistance heating in a long wire (length = 5 m, diameter = 2 mm). This wire is wrapped with an insulation of thickness 1 mm that has a thermal conductivity of 0.1 W/m.K. The insulated wire is exposed to air at 30°C. The convective heat transfer between the wire and surrounding air is characterized by a heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/m2.K. The temperature (in °C) at the interface between the wire and the insulation is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

