GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Chemical
- The local velocity of a fluid along a streamline can be measured by
- In a mixing tank operating at very high Reynolds number (> 104), if the diameter of the impeller is doubled (other conditions remaining constant), the power required increases by a factor of
- For heat transfer across a solid-fluid interface, which one of the following statements is NOT true when the Biot number is very small compared to 1?
- A solid sphere with an initial temperature Ti is immersed in a large thermal reservoir of temperature T0. The sphere reaches a steady temperature after a certain time t1. If the radius of the sphere is doubled, the time required to reach steady-state will be
- In the McCabe-Thiele diagram, if the x -coordinate of the point of intersection of the q -line and the vapor-liquid equilibrium curve is greater than the x -coordinate of the feed point, then the quality of the feed is
-
For which of the following combinations, does the absorption operation become gas-film controlled? P. The solubility of gas in the liquid is very highQ. The solubility of gas in the liquid is very lowR. The liquid-side mass transfer coefficient is much higher than the gas-side mass transfer coefficientS. The liquid-side mass transfer coefficient is much lower than the gas-side mass transfer coefficient
- The half-life of an nth order reaction in a batch reactor depends on
-
Consider the reaction scheme shown below
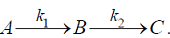 Both the reactions are first-order. The activation energies for k1 and k2 are 80 and 20 kJ/mol, respectively. To maximize the yield of B, it is preferable to use
Both the reactions are first-order. The activation energies for k1 and k2 are 80 and 20 kJ/mol, respectively. To maximize the yield of B, it is preferable to use - In petroleum refining, catalytic reforming is used to convert
- The final boiling points of gasoline, diesel, atmospheric gas oil (AGO) and lubricating oils vary as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

