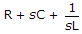ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
For an RC admittance function
-
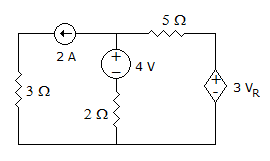
Norton's equivalent circuit
-
The poles and zeros of a positive real functions are real or occur in conjugate pair.
-
A coil is connected across a 200 V, 50 Hz supply and takes a current of 10 A. The loss in the coil is 1000 W. The impedance and resistance of the coil are
-
Consider the following: Energy storage capability of basic passive elements is due to the fact that
- resistance dissipates energy
- capacitance stores energy
- inductance dissipates energy
-
In an ac circuit that delivers constant power at varying p.f., the current is
-
The parameter A of a two port network is equal to


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook