ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
In a circuit with capacitance connected to ac source, the rate of change of capacitor voltage is constant.
-
Assertion (A): If Z1(s) and Z2(s) are positive real then Z1(s) + Z2(s) as well as 1/Z1(s) and 1/Z2(s) are positive real.
Reason (R): The poles of a positive real function are real or occur in conjugate pairs.
-
A variable resistance R and capacitive reactance XC are connected in series. As R is varied, the locus of Z is
-
Kirchoff's laws are applicable to
-
The double energy transients occur in the
-
The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor varies as per the equation C(t) = C0 (1 - cos ωt). It is connected to a battery of V volts. The equation for current is
-
Which one of the following is a passive device/Component?
-
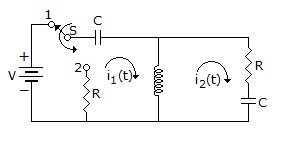
Which one of the following theorem can be conveniently used to calculate the power consumed by the 10 Ω resistor in the network shown in the above figure?


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook