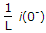ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
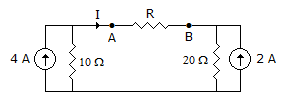
In figure, the current I
-
Consider the following statements
- Current through inductor cannot change abruptly.
- Voltage across capacitor cannot change abruptly.
- Initial value of f(t) is
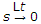 sF (s).
sF (s). - Final value of f(t) is
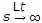 sF (s).
sF (s).
-
As B is increased from zero to about 2T, μr, of a ferromagnetic material
-
In open circuit impedance parameters, the independent variables are
-
An RLC series circuit is excited by a step voltage E. The initial current through L is i (0-). In the s domain circuit the element L will be replaced by
-
If two networks are connected in parallel then equivalent y parameter of both is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook