ECE :: Network Analysis and Synthesis
-
If Va1 = Va2 = 100 V and Va0 = 0, then Va, Vb, Vc are
-
Assertion (A): A series RLC circuit resonates when excited by variable frequency source.
Reason (R): Resonant frequency is geometric mean of half power frequencies.
-
In figure, the switch S is initially open and steady state conditions are reached. At t = 0 switch is closed. The initial current through 2C capacitor is
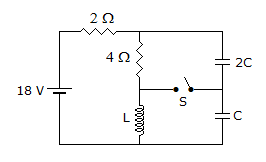
-
For an RC driving point impedance function, the poles and zeros
-
In the circuit of figure the current through 5 Ω resistance at t = ∞ is
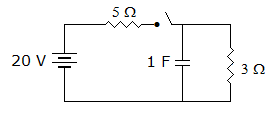
-
In h parameter representation, the independent variables are
-
For maximum transfer of power, internal resistance of the source should be
-
The Laplace transform of a continuous-time signal x(t) is
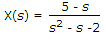 If the Fourier transform of this signal exists, then x(t) is
If the Fourier transform of this signal exists, then x(t) is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

