Civil Engineering :: Theory of Structures
-
A composite beam is composed of two equal strips one of brass and other of steel. If the temperature is raised
-
A two hinged parabolic arch of span l and rise h carries a load varying from zero at the left end to ω per unit run at the right end. The horizontal thrust is
-
The force in EC of the truss shown in the given figure, is
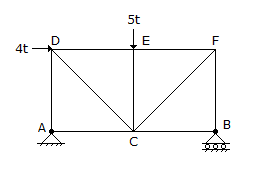
-
Shear centre of a half circular section of radius r and of constant thickness, lies at a distance of x from the centre where x is
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
-
The forces acting on the bar as shown in the given figure introduce
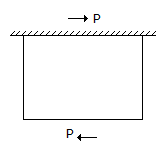
-
The equation of a parabolic arch of span l and rise h, is given by
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
-
The horizontal thrust on the ends of a two hinged semicircular arch of radius R carrying
-
Maximum principal stress theory for the failure of a material at elastic point, is known
|
A.
The moment of inertia is calculated about the axis about which bending takes place |
|
B.
If tensile stress is less than axial stress, the section experiences compressive stress |
|
C.
If tensile stress is equal to axial stress, the section experiences compressive stress |
|
D.
If tensile stress is more than axial stress, some portion of the section experiences a tensile stress |
|
E.
All the above. |
|
A.
a uniformly distributed load ω per unit run over its right half span, is \( \frac { 2 } { 3 } \) \( \frac { wR } { n } \) |
|
B.
a uniformly distributed load ω per unit run over its right half span, is \( \frac { 4 } { 3 } \)\( \frac { wR } { n } \) |
|
C.
a distributed load varying from zero at the left end to ω per unit horizontal run at the right end, is \( \frac { 2 } { 3 } \) \( \frac { wR } { n } \) |
|
D.
all the above. |


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

