Civil Engineering :: Theory of Structures
-
A road of uniform cross-section A and length L is deformed by δ, when subjected to a normal force P. The Young's Modulus E of the material, is
-
The S.F. diagram of a loaded beam shown in the given figure is that of
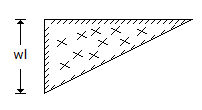
-
An isolated load W is acting at a distance a from the left hand support, of a three hinged arch of span 2l and rise h hinged at the crown, the horizontal reaction at the support, is
-
The ratio of lateral strain to axial strain of a homogeneous material, is known
-
For beams of uniform strength, if depth is constant,
-
The area of the core of a column of cross sectional area A, is
-
A simply supported beam carries a varying load from zero at one end and w at the other end. If the length of the beam is a, the shear force will be zero at a distance x from least loaded point where x is
-
The locus of reaction of a two hinged semi-circular arch, is
-
The ratio of the area of cross-section of a circular section to the area of its core, is
-
The yield moment of a cross section is defined as the moment that will just produce the yield stress in


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

