Civil Engineering :: Theory of Structures
-
For permissible shear stress fs, the torque transmitted by a thin tube of mean diameter D and wall thickness t, is
-
A compound bar consists of two bars of equal length. Steel bar cross-section is 3500 mm2 and that of brass bar is 3000 mm2. These are subjected to a compressive load 100,000 N. If Eb = 0.2 MN/mm2 and Eb = 0.1 MN/mm2, the stresses developed are:
-
p = \(\frac { n^2EI } { L^2 }\)is the equation for Euler's crippling load if
-
Flat spiral springs
-
A simply supported uniform rectangular bar breadth b, depth d and length L, carries an isolated load W at its mid-span. The same bar experiences an extension e under same tensile load. The ratio of the maximum deflection to the elongation, is
-
A cantilever of length 2 cm and depth 10 cm tapers in plan from a width 24 cm to zero at its free end. If the modulus of elasticity of the material is 0.2 x 106 N/mm2, the deflection of the free end, is
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
-
A simply supported rolled steel joist 8 m long carries a uniformly distributed load over it span so that the maximum bending stress is 75 N/mm2. If the slope at the ends is 0.005 radian and the value of E = 0.2 x 106 N/mm2, the depth of the joist, is
-
A square column carries a load P at the centroid of one of the quarters of the square. If a is the side of the main square, the combined bending stress will be
-
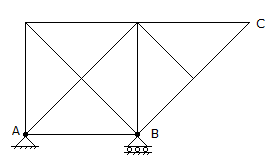
The degree of indeterminacy of the frame in the given figure,
|
A.
The bending stress in a section is zero at its neutral axis and maximum at the outer fibres |
|
B.
The shear stress is zero at the outer fibres and maximum at the neutral axis |
|
C.
The bending stress at the outer fibres, is known as principal stress |
|
D.
The planes of principal stresses are inclined at 45° to the neutral plane |
|
E.
All the above. |

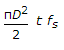
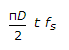
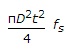

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

