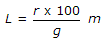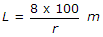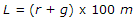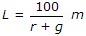Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
If the velocity of moving vehicles on a road is 24 km/per hour, stopping distance is 19 metres and average length of vehicles is 6 metres, the basic capacity of lane, is
-
If the rate of change of grade permitted along a vertical curve is r and total change of grade is g%, the length L of the curve to be provided, is
-
In case of a multi-lane road, overtaking is generally permitted
-
The pavement width of a road depends upon
-
For a vehicle moving with a speed of 80 km per hour, the brake reaction time, in ordinary cases, is
-
The desirable camber for straight roads with thin bituminous surfacing, is
-
Minimum stopping distance for moving vehicles on road with a design speed of 80 km/hour, is
-
If the radii of a compound curve and a reverse curve are respectively the same, the length of common tangent
-
If cross slope of a country is greater than 60%, the terrain is classified as
-
Side drains on both sides of a hill road, are essential when the road is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook