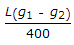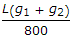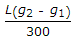Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
Minimum thickness of the base of a flexible pavement, is
-
One-way streets are generally provided in crowded cities as, these
-
The perpendicular offset from the tan-get to the central point of the circular curve, is
-
An Executive Engineer of roads, executes works under direct control of
-
Newly constructed pavement with ordinary Portland cement attains its working strength after
-
Curves in the same direction separated by short tangents, are called
-
When an up gradient of a highway meets a downgrade, the vertical curve provided, is known as
-
If the coefficient of friction on the road surface is 0.15 and a maximum super-elevation 1 in 15 is provided, the maximum speed of the vehicles on a curve of 100 metre radius, is
-
The maximum distance of the apex of a vertical curve of length L from the point of intersection of two grades + g1%, and - g2% (g1 > g2), is
-
The wall constructed for the stability of a back filling portion of a road on the down hill side, is known as


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook