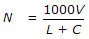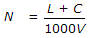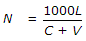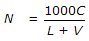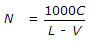Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
If no super elevation is provided on a road along curves, pot holes may develop at
-
The width of road pavements, depends upon
-
If L is the length of vehicles in metres, C is the clear distance between two consecutive vehicles (stopping sight distance), V is the speed of vehicles in km/hour, the maximum number N of vehicles/hour, is
-
The minimum vertical clearance of overhanging cliffs or any other structure above the surface of a hill road, should be
-
Speed regulations on roads is decided on the basis of
-
Reconnaissance is best done with the help of
-
The usual width of side drains along Highways in hilly region, is
-
Normal formation width of a hill road for one-way traffic, is
-
The most commonly adopted method to provide super-elevation on roads, is by pivoting the road surface about


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook