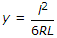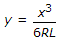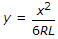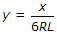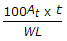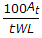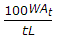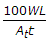Civil Engineering :: Highway Engineering
-
If a Lemniscate curve of transition throughout is introduced to connect two parallel roads, the maximum polar angle of the curve, is
-
If the cross slope of a country is 25% to 60%, the terrain is classified as
-
Setting out of Lemniscate transition curves, is done with
-
Reference pillars fixed on the centre line of a proposed road, provide the following information:
-
The normal road land width for a major district road in open area, is
-
On earth roads, the camber should preferably be
-
The convexity provided to the carriageway between the crown and edge of the pavement, is known as
-
Alignment of highways in hilly regions, is decided on
-
The standard equation of a cubical spiral transition curve provided on roads, is
-
If At is the area of steel cross-section, t is working stress, L is width of road and W is weight of slab per square metre, the spacing of the tie bars for a longitudinal joint, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook