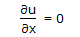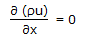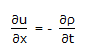Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
Which of the following two quantities when same, makes one pipe system equivalent to another pipe system ?
-
The kinetic energy correction factor for velocity distribution of laminar flow is
-
Priming of a centrifugal pump is done to
-
Bed pressure drop in an air fluidised bed of catalyst particles (ρp = 200 kg/m3, Dp = 0.05 cm) of 60 cm bed depth and bed porosity of 0.5 expressed in cm of water (manometer) is
-
For pipes that must be broken at intervals for maintenance, the connector used should be a/an
-
A fluid is the one, which
-
One horsepower is equal to
-
For one dimensional flow of an incompressible fluid in unsteady state in x-direction, the continuity equation is given by
-
A fluid
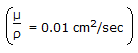 is moving at critical flow condition (NRe = 2100) through a pipe of dia 3 cms. Velocity of flow is __________ cm/sec.
is moving at critical flow condition (NRe = 2100) through a pipe of dia 3 cms. Velocity of flow is __________ cm/sec. -
Capillary rise of mercury in a small diameter tube is proportional to (where, d = diameter of the tube, σ = surface tension of mercury)


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook