Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
The ratio of the depth of flow to the diameter of the channel for maximum discharge in a circular channel in open channel flow is
-
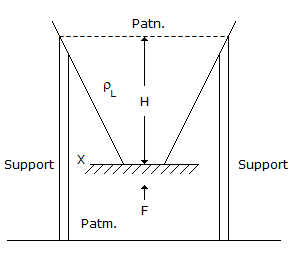
A conical tank with a bottom opening of cross-sectional area A is filled with water and is mounted on supports as shown in the figure. What is the force F with which plate X must be pushed up to prevent water from leaking ? Assume that the density of air is negligible as compared to the density of water ρL.
-
A relief valve
-
An isentropic process is the one, in which
-
The distribution of shear stress in a stream of fluid in a circular tube is
-
For motion of spherical particles in a stationary fluid, the drag co-efficient in hindered settling compared to that in free settling is
-
Specific speed of a centrifugal pump relates it with another pump having the
-
Air vessel fitted to a reciprocating pump
-
Deformation drag, which is caused by widespread deformation of fluid around the immersed body
-
In isotropic turbulence, the __________ are equal to each other.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

