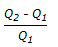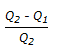Chemical Engineering :: Fluid Mechanics
-
The continuity equation of fluid mechanics utilises the principle of conservation of
-
Which of the following is not a dimension-less parameter ?
-
In which of the following cases, it is possible for flow to occur from low pressure to high pressure ?
-
The percentage slip in a reciprocating pump set is given by the % of (where, Q1 = actual discharge Q2 = theoretical discharge)
-
The blades of a centrifugal impeller are said to be curved forward, if the __________ of the motion of impeller blades.
-
For the same terminal conditions and fitting size, the least friction loss is incurred in a/an
-
A floating/submerged body is always stable, if its centre of gravity
-
The co-efficient of discharge of an orificemeter is a function of
-
Critical velocity in a pipe flow


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook