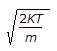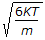Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
For equilibrium process (i.e. reversible) in an isolated system
-
The partial molar enthalpy of a component in an ideal binary gas mixture of composition Z, at a temperature T and pressure P, is a function only of
-
With increase in reduced temperature, the fugacity co-efficient of a gas at constant reduced pressure
-
For an ideal gas, the enthalpy
-
Efficiency of a heat engine working on Carnot cycle between two temperature levels depends upon the
-
In Joule-Thomson porous plug experiment, the
-
The root mean square speed of molecules of a gas is equal to (where, m = mass of the molecule K = Boltzman's constant, T = absolute temperature)
-
The intensive properties are
-
A Carnot cycle consists of the following steps :
-
For a cyclic process, a fixed ratio between heat and work


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook