Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
The Carnot co-efficient of performance (COP) of a domestic air conditioner compared to a household refrigerator is
-
The unit of fugacity is the same as that of the
-
Filling of gas from a high pressure cylinder into small bottles is an example of a/an __________ process.
-
A large iceberg melts at the base, but not at the top, because of the reason that
-
At the critical point of a substance
-
A system undergoes a change from a given initial state to a given final state either by an irreversible process or by a reversible process, then(where, Δ S1 and Δ SR are the entropy changes of the system for the irreversible and reversible processes respectively)
-
A two stage compressor is used to compress an ideal gas. The gas is cooled to the initial temperature after each stage. The intermediate pressure for the minimum total work requirement should be equal to the __________ mean of P1 and P2.(where, P1 and P2 are initial and final pressures respectively)
-
y = specific heat ratio of an ideal gas is equal to
-
Consider the process A & B shown in the figure given below
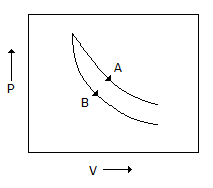
In this case, it is possilbe that -
Gibbs free energy of a pure fluid approaches __________ as the pressure tends to zero at constant temperature.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

