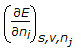Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
All gases during throttling process at atmospheric temperature and pressure show a cooling effect except
-
Compressibility factor for almost all the gases are approximately same at the same
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
The co-efficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerating system, which is its index of performance, is defined as the ratio of useful refrigeration to the net work. The units of __________ and COP are the same.
-
The chemical potential of a component (μi) of a phase is the amount by which its capacity for doing all work, barring work of expansion is increased per unit amount of sustance added for an infinitesimal addition at constant temperature and pressure. It is given by
-
In jet refrigerators, the refrigerating fluid is practically always
-
Pick out the correct statement.
|
A.
Compression ratio of an Otto engine is comparatively higher than a diesel engine.
|
|
B.
Efficiency of an Otto engine is higher than that of a diesel engine for the same compression ratio.
|
|
C.
Otto engine efficiency decreases with the rise in compression ratio, due to decrease in work produced per quantity of heat.
|
|
D.
Diesel engine normally operates at lower compression ratio than an Otto engine for an equal output of work.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook