Chemical Engineering :: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
-
Boyle's law for gases states that
-
1st law of thermodynamics is nothing but the law of conservation of
-
In a reversible chemical reaction (where, Δx = number of moles of products-number of moles of reactants )
-
Out of the following refrigeration cycles, which one has maximum COP ?
-
Pick out the correct statement:
-
In any spontaneous process,
-
Which of the following is a thermodynamic property of a system ?
-
Equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature
-
The expression,
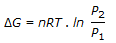 , gives the free energy change
, gives the free energy change
|
A.
In an isothermal system, irreversible work is more than reversible work.
|
|
B.
Under reversible conditions, the adiabatic work is less than isothermal work.
|
|
C.
Heat, work, enthalpy and entropy are all 'state functions'.
|
|
D.
Matter and energy can not be exchanged with the surroundings in a closed system.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


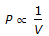 , when temperature is constant.
, when temperature is constant. 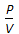 = constant, for any gas.
= constant, for any gas.