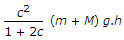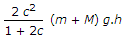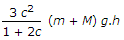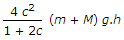Mechanical Engineering :: Theory of Machine
-
In a disc clutch, if there are n1 number of discs on the driving shaft and n2 number of discs on the driven shaft, then the number of pairs of contact surfaces will be
-
The effect of swaying couple in a locomotive is resisted by the side pressure between the flanges of the tyres of the wheel and the inside of the rails.
-
The Klein's diagram is useful to find
-
The equation of motion for a single degree of freedom system with viscous damping is
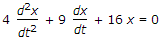 . The damping ratio of the system is
. The damping ratio of the system is -
The ratio of the number of teeth to the pitch circle diameter in millimetres, is called
-
The ratio of the pitch circle diameter in millimetres to the number of teeth, is called circular pitch.
-
The rotating shafts tend to vibrate violently at whirling speeds because
-
Which of the following is an inversion of a double slider crank chain?
-
The unbalanced force due to revolving masses


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook