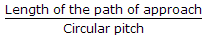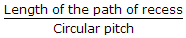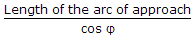Mechanical Engineering :: Theory of Machine
-
The pitching of a ship produces forces on the bearings which act __________ to the motion of the ship.
-
The two links OA and OB are connected by a pin joint at O. If the link OA turns with angular velocity ω1 rad/s in the clockwise direction and the link OB turns with angular velocity ω2 rad/s in the anti-clockwise direction, then the rubbing velocity at the pin joint O is (where r = Radius of the pin at O)
-
When the two elements of a pair have __________ when in motion, it is said to a lower pair.
-
The ratio of maximum fluctuation of energy to the workdone per cycle is called
-
In a steam engine, the earlier cut-off with a simple slide valve may be obtained by increasing the steam lap and the angle of advance of the eccentric but keeping constant the travel and lead of the valve, This method will


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook